ct scan results if serious
 How Long Does a CT Scan of the Abdomen Take? - American Health Imaging
How Long Does a CT Scan of the Abdomen Take? - American Health ImagingComputed Tomography (Computed Tomography) What is a CT scanner? A computed tomography (CT or CAT) uses computers and rotary X-ray machines to create cross-sectional images of the body. These images provide more detailed information than normal X-ray images. They can show soft tissues, blood vessels and bones in various parts of the body. You can use a CT scan to view:During a CT scan, you are in a machine similar to the tunnel while the inside of the machine rotates and takes a series of X-rays from different angles. These images are sent to a computer, where they are combined to create slice images or cross-sections of the body. They can also be combined to produce a 3-D image of a particular area of the body. Computed tomography has many uses, but it is especially suitable for diagnosing diseases and evaluating injuries. The imaging technique can help your doctor: The test is minimally invasive and can be done quickly. Your doctor may give you a special dye called contrast material to help internal structures appear more clearly in X-ray images. The contrast material blocks the X-rays and appears white in the images, allowing it to highlight the intestines, blood vessels or other structures in the area under review. Depending on the part of your body that is being inspected, you may need to drink a fluid that contains the contrast. Alternatively, the contrast may need to be injected into your arm or administered through your rectum through an enema. If your doctor plans to use a contrast material, you may ask you to accelerate for four to six hours before your CT. When the time comes to perform the CT scan, you will be asked to change into a hospital gown and remove any metallic objects. Metal can interfere with the results of the CT scan. These items include jewelry, glasses and dentures. Your doctor will ask you to lie on a table that slides towards the CT scanner. They'll leave the exam room and go to the control room where they can see you and listen to you. You can communicate with them through an intercom. As the table slowly moves you to the scanner, the X-ray machine will spin around you. Each rotation produces numerous images of thin slices of your body. You can hear clicking on, buzzing and noise buzzing during exploration. The table will move a few millimeters at a time until the test is finished. The whole procedure can take anywhere from 20 minutes to an hour. It is very important to remain still while TC images are taken because the movement can result in blurry images. Your doctor may ask you to keep your breath for a short period of time during the test to prevent your chest from moving up and down. If a young child needs a CT scan, the doctor may recommend a sedative to prevent the child from moving. Once the CT scan is finished, the images are sent to a radiologist to be examined. A radiologist is a doctor who specializes in diagnosing and treating conditions using imaging techniques, such as computed tomography and X-ray. Your doctor will follow you to explain the results. There are very few risks associated with a CT scan. Although computed tomography exposes you to more radiation than typical X-rays, the risk of radiation-caused cancer is very small if you only have a scan. Your risk of cancer may increase over time if you have multiple X-rays or CT scans. The risk of cancer increases in children receiving CT scans, especially in the chest and abdomen. Some people have an allergic reaction to contrast material. Most contrast material contains iodine, so if you have had an adverse reaction to iodine in the past, make sure to notify your doctor. Your doctor may give you allergy or steroid medications to counter any potential side effect if you are allergic to iodine, but you should be contrasted. It is also important to tell your doctor if you are pregnant. Although the radiation of a CT scan is unlikely to damage your baby, your doctor may recommend another test, such as ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging, to minimize risk. The results of the CT scan are considered normal if the radiologist did not see any tumor, blood clots, fractures, or other abnormalities in the images. If anomalies are detected during CT scan, more tests or treatments may be needed, depending on the type of anomaly found. Last medical review on 25 February 2016Read this following

CT scan or CAT scan: How does it work?
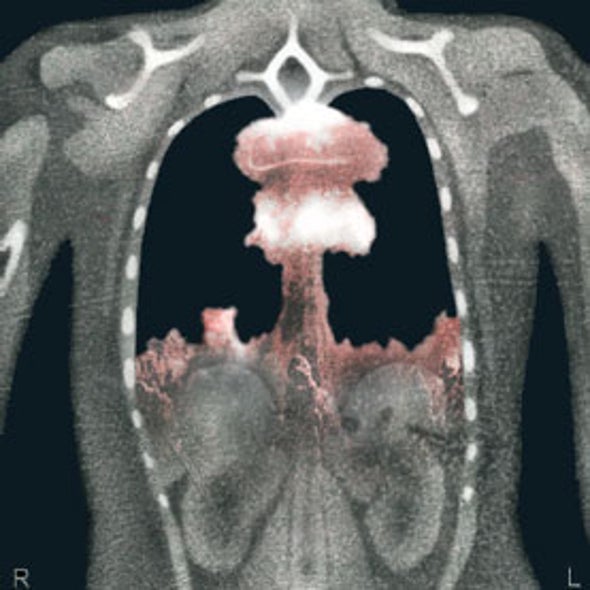
How Much Do CT Scans Increase the Risk of Cancer? - Scientific American

CT scan brain (plain and contrast images) showing multiple lesions... | Download Scientific Diagram

When the Results of PET and CT Scans Do Not Tell the Same Story | CANCER STORY
CT scan - NHS

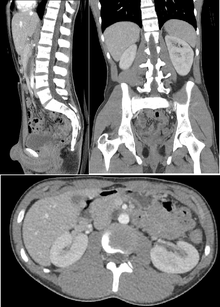
CT of the Abdomen/Pelvis | Cedars-Sinai
How to interpret CT scans of your lung

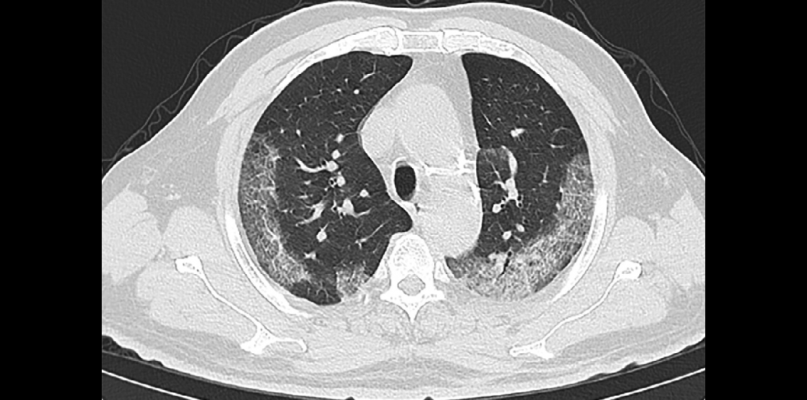
Chest CT in COVID-19: What the Radiologist Needs to Know | RadioGraphics

Abdominal CT scans: Definition, uses, picture, and more
Diagnosis, Results and Treatment - Northern Health and Social Care Trust

CT lung screening cuts cancer mortality 51% in Japan | East River Medical Imaging

Startradiology

Headache, MRI and Brain Imaging
How to interpret an unenhanced CT Brain scan. Part 1: Basic principles of Computed Tomography and relevant neuroanatomy
CT scan or CAT scan: How does it work?
What Are Common Reasons for an Abnormal CT Scan?
Lymphoma Action | Scans: X-ray, CT, PET and MRI
/2252467_color2-5bc4a212c9e77c00528a71be.png)
PET Scan: Uses, Side Effects, Procedure, Results
CT Scan | Internet Stroke Center
CT scan - Wikipedia
Delayed reading of MRI, CT Scan or X-Ray Can Result in Death or Serious Injury - Schwaner Injury Law
CT vs MRI: What's the Difference? And How Do Doctors Choose Which Imaging Method to Use? | Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center

PATIENT EDUCATION FOR C.T. SCAN What is a CT or CAT scan
Computed Tomography (CT or CAT) Scan of the Brain | Johns Hopkins Medicine

Anyone explain me the results of mri report (attached with question)? - Quora
New Research Advocates for Chest CT in COVID-19 Diagnosis | Imaging Technology News
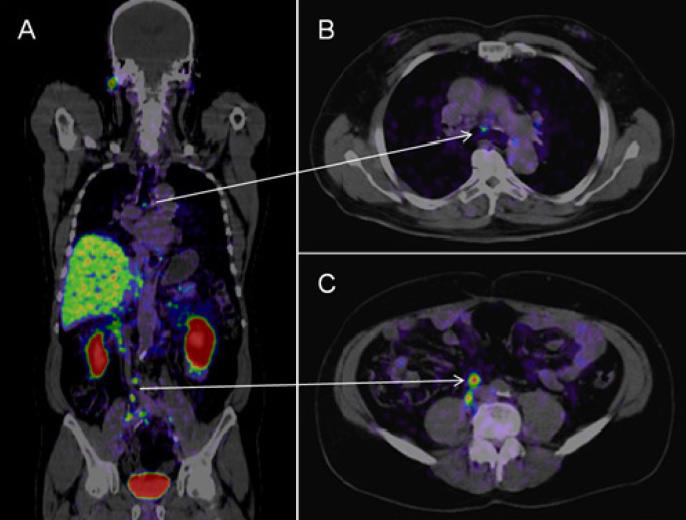
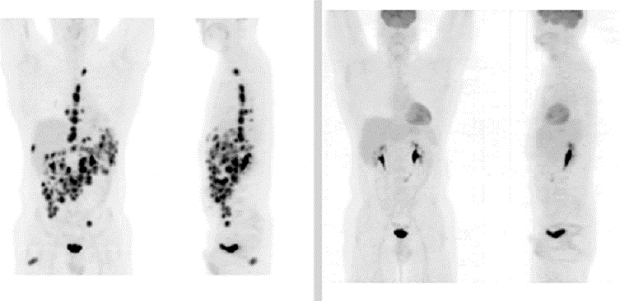
PSMA PET-CT Accurately Detects Prostate Cancer Spread - National Cancer Institute
CT Scans vs. MRIs: Differences, Benefits, and Risks

Framingham Cohort dbGaP Study Accession: phs000007.v22.p8 Note: This version of the study has been superseded. See most recent version Request Access Study version history Study phs000007.v1.p1 phs000007.v2.p1 phs000007.v3.p2 phs000007 ...

MRI vs. CT Scan | Health Images
Abdominal CT Scan with Contrast: Purpose, Risks, and More

Radiological findings from 81 patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study - The Lancet Infectious Diseases

Having an Exam That Uses Contrast Dye? Here's What You Need to Know
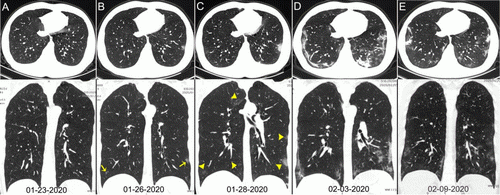
CT Provides Best Diagnosis for Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) | Imaging Technology News
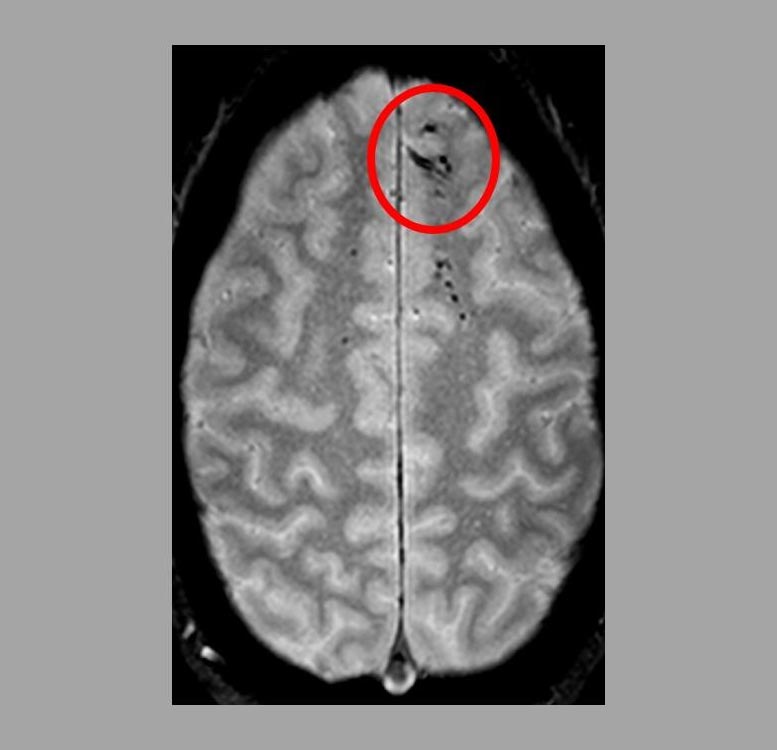
Microbleeds – Too Small to Be Detected on CT Scans – May Worsen Outcome After Head Injury

Problems with CT Scans for Cancer Diagnosis
CT Scans vs. MRIs: Differences, Benefits, and Risks

CT scans might offer a more accurate way to diagnose Covid-19 - STAT
Problems with CT Scans for Cancer Diagnosis
AI Learns from Lung CT Scans to Diagnose COVID-19 | The Scientist Magazine®
Posting Komentar untuk "ct scan results if serious"